|
|
cockroach pest control methods |
| Cockroaches are obnoxious pests... |
|
Y U C K ... Cockroaches are known carriers of serious
diseases, such as, salmonella, dysentery, gastroenteritis and other stomach complaint
organisms. They adulterate food and spread pathogenic organisms with their feces
and defensive secretions.
Asthmatic reactions: Cockroaches must molt regularly throughout their life-cycle. The discarded skin becomes airborne and can cause severe asthmatic reactions, particularly to children, the elderly and people with bronchial ailments. The cockroach begins as an egg: The female produces an egg sac which she carries or deposits in a safe place. The young cockroach or "nymph" will undergo a series of molts, shedding it's external skeleton, as it grows to adulthood. The entire life cycle may extend to a few months depending on the species and environmental factors, such as, access to food and moisture, adequate shelter and warm temperatures. Even the cleanest homes get'em: Cockroach pests and their eggs are spread throughout the community in food and other packaging. Although sanitation and hygiene are important deterrents, even the cleanest homes become infested with cockroaches due to minute deposits of grease, sugar and other food deposits in difficult to get at places, such as, in drains, behind refrigerators and dishwashers, inside cracks and crevices in kitchen cupboards. Omnivorous by nature: Cockroaches will eat almost any organic matter no matter how rancid. Once inside the home, they will seek out food scraps, unsealed food containers, sugar and grease deposits, pet food, rancid meat, glue and even book bindings. YUCK...they eat each others feces, to feed the young "nymphs" and extract all nourishment from an organic food source. If you see a clump of pepper-like specs in your kitchen cupboards, it is likely cockroach feces marking their courtship and nearby nesting territory. Nocturnal feeders: Cockroaches rest during daylight hours in dark warm secure harborages in your home, such as, in wall cavities, the sub-floor, roof void, cracks and crevices in the kitchen and bathroom, electrical appliances and foodstuffs. They will emerge from these harborages in the still of the night. Cockroaches have an array of acute sensory and survival instincts. If you see cockroaches in your home during the day, you have a serious problem. Rapid breeding cycle: If left unchecked a cockroach infestation can rapidly expand it's numbers in a few weeks or months to become major risk to health and safety. |
| Professional Pest Control: Cockroaches |
The IGR bait is an insect growth regulator that stops the ability of the cockroach to replace its skin - made of "chitin". These IGR's are of ultra low toxicity to people. Applied as small blobs in cockroach habitat areas away from human contact, the gel-bait is highly attractive to cockroaches and provides effective control, usually for many months. Permethrin dust: In some cases, we recommend the use of a synthetic pyrethroid (permethrin) dust inside roof voids and under floors. Permethrin dust is modeled on the natural extract of pyrethrum flower and if used in accordance with label directions is one of the safest insecticides (to humans, dogs and cats) commercially available. Low concentrations (2 percent) of permethrin, as in flea sprays labeled "for cats," are not considered toxic to cats. It is only the spot-on flea products that contain high concentrations (45 to 65 percent) of permethrin and are approved for use on "dogs only" that are considered dangerous. How much does it cost? Onsite appraisal is need to determine the exact cost. The treatment cost depends on size of the house, ease of access to various parts of the building. Commercial premises need to be appraised on a specific basis. |
|
| What the Home Owner can do |
| Inspection: first, inspect the entire kitchen area, under sinks, refrigerator,
dishwasher, stove, microwave oven, other cooking appliances, bathroom cabinets,
draws, basement and sub-floor crawlspace (if any) for likely high activity
and harborage areas. Look for cockroaches, alive or dead, their feces and
egg sacs.
Identification: place "sticky" glue traps in any likely high activity areas. At night sneak into the kitchen, turn on the lights and observe any cockroach activity. Observe where they scurry to. Place your sticky traps near these areas to collect and identify the species and the source of infestation. Food, shelter and water - we all need it, so do cockroaches. Make your home unfit for cockroaches, where possible, take away their food, water and restrict shelter and access points into the kitchen and they will almost certainly move somewhere else. Starve them out - keep all food in sealed containers. Particularly at night, do not leave food scraps exposed in the kitchen or waste storage areas. Thoroughly clean all benches and food preparation areas, particularly between counters and appliances. Regularly vacuum accessible likely harborage and high activity areas, carpets, drapes, furniture, kitchen and bathroom cupboards in order to remove cockroach eggs and food deposits. Cockroaches need water and will thrive in damp sub-floor crawl space areas, near leaking taps, etc. Ensure adequate drainage and ventilation. Regularly check and fix any plumbing problems, broken roof tiles, etc that may allow or cause moisture ingress to potential cockroach harborage areas. Wipe kitchen sink of moisture before retiring or going out at night. Turn off leaking taps. Reduce shelter and access points: seal all cracks and crevices in bathroom, pantry and kitchen cupboards. Store all cardboard boxes and the like above ground level. Cockroaches do not like drafty exposed areas, nor bright lights. A good reason why some restaurants keep lights on at night around their dumpster waste bins. |
| Cockroach Species Identification |
| Correct identification is essential: There are several cockroach pest species that infest domestic and commercial premises. The identification of each species is necessary to best determine likely harborage areas and an effective pest control program. |
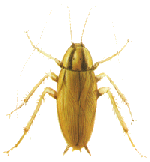
German
cockroach --- Blatella germanica
|
World best traveler? The German cockroach is the most widely transported insect pest in the world. Infestations even occur in Alaska, in larger installations with central heating or around machinery that produces heat. In warmer climates, it is commonly found in homes, apartments, restaurants, food processing plants, supermarkets and warehouses. Their eggs arrive in food containers, cartons, fridges, stoves and other appliances or materials brought into a building. Habitat: German cockroaches are unable to survive in locations away from humans or human activity. German cockroach infestations usually occur in bathrooms and kitchens. They like to hide-out during the day in tight secure places. Their daytime harborage areas are usually near a food and moisture source, such as, inside wall cavities, behind baseboards, cracks and crevices in pantry, kitchen and bathroom cupboards, and under electrical, heating and cooking appliances. Rapid breeding cycle: The German cockroach is the most prolific breeder among all cockroaches. The female German cockroach lives up to 6 months. She carries an egg capsule containing 30 to 40 eggs. Development from egg to adult can occur in 45 days, during which they molt 6 times. The German cockroach will breed rapidly throughout the year, but favors a humid environment of around 80F or warmer. An small initial infestation can become a major problem in a few months. |
|
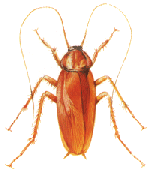
American
cockroach --- Periplaneta americana
|
Habitat: Preferred daytime habitat locations include the sub-floor, basement, in sewers and other warm, dark, moist locations. They avoid cold areas but will thrive outdoors in temperatures above 80F. Indoors they often congregate around hot water pipes, fridge motors, boilers and other heating appliances. The American cockroach will feed on a wide variety of plant and animal material. Rapid breeding cycle: The female life span up to 1.5 years; incubation period of eggs 6 to 8 weeks; in ideal conditions they quickly reach plague proportions. |
|
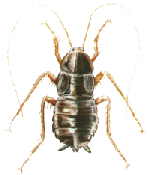
Oriental
cockroach --- Blatta orientalis
|
Habitat: Most often found in dark basements or cellars, but can also climb garbage chutes, sewer and water pipes to the upper floors in high-rise buildings. Oriental cockroaches prefer to feed on starchy foods. Rapid breeding cycle: The female lives up to 2 years; deposits up to 18 egg-sacs in lifetime; each egg sac contains 16 eggs; incubation period is 1 to 2 months; development period is 12 months, undergoing 7 molts. An infestation will rapidly expand in ideal conditions, particularly during the warm summer months with temperatures regularly above 80oF. |
|
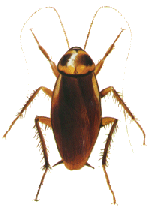
Australian
cockroach --- Periplanta australasiae
|
Habitat: Generally prevalent in areas where winters are relatively mild. However, in colder climates they are prevalent in greenhouses and near large heating apparatus, air-conditioners or other equipment emitting heat constantly. They are opportunistic fliers and will infest anywhere adequate heat, humidity and food supply is available. Prime areas of interest are often pet food bowls and food waste storage areas. Rapid breeding cycle: The female lives up to 6 months; incubation period of eggs 40 days. An infestation can rapidly expand in ideal conditions, particularly during the warmer climates when temperatures are regularly above 80F. Chronic household infestations usually emanate from the roof void, attic or sub-floor areas of the building. |
|
| Links to websites on cockroaches |
|
Colorado
State University - expert information and advice on cockroach pest
species, cockroach control methods, residual insecticidal sprays, dusts and baits,
preventive measures and house maintenance tips.
Cornell University - excellent website providing information on cockroach pest species; integrated pest management procedures applicable to cockroach control; and references to leading textbooks and articles. New Mexico State University - information on cockroaches and pest control products. University of Alaska - yes, there are cockroach problems in Alaska. The University of Alaska entomology department discusses the cockroach pest species found in Alaska and the methods of control. University of California - excellent comprehensive website providing a detailed analysis of cockroach pest species, cockroach pest control products and procedures, non-chemical housekeeping and maintenance recommendations. |
| Learn about other common household pests |
| Ants | Borers | Silverfish | |||
 |
Bed Bugs | Roaches | Spiders | ||
| Bees | Fleas | Termites | |||
| Bird Control | Rats & Mice | Wasps |
| |
| Published by Fumapest Group © copyright 1995 - updated: |