| Nevada dampwood termites |
| Zootermopsis nevadensis |
Primarily a forest dwelling termite this termite is the common termite found in the Californian mountains. Higher and drier altitudes are preferred, ranging up to 9,000 feet above sea level. Identification of Swarmers and Soldiers: Soldiers are similar in appearance to the Pacific dampwood termite, but with longer heads with straighter sides. The swarmer is a darker brown than the Pacific dampwood termite. Identification of Timber Damage: The appearance of the damage inflicted upon timbers by this species is very similar to the Pacific dampwood termite. Biology and Habits: This species is very similar in habit to the Pacific Dampwood termite. This species will attack wood of all types throughout its range. Timbers in contact with the soil or structures built near or over water are common targets. This species is known to be very tolerant of moist conditions, even being found in pilings subject to tidal flooding. Colony size varies but may contain as many as 4,000 individuals. Colony growth is aided by the production of secondary reproductives. Like other termites this species aid in the spreading of wood decay fungi, the spores of which are carried in the gut and on their bodies. A well established colony will produce winged reproductives which may infest nearby timber. |
| About Termites in Your Local Area |
| CLICK ON YOUR STATE:
Alabama -
Arizona -
Arkansas -
northern California - southern
California -
Colorado -
Connecticut -
Delaware -
Florida -
Georgia -
Hawaii -
Idaho -
Illinois -
Indiana -
Iowa -
Kansas -
Kentucky -
Louisiana -
Maine -
Maryland -
Massachusetts -
Michigan -
Minnesota -
Mississippi -
Missouri -
Montana -
Nebraska -
Nevada -
New Hampshire -
New Jersey -
New Mexico -
New York -
North Carolina -
North Dakota -
Ohio -
Oklahoma -
Oregon -
Pennsylvania -
Rhode Island -
South Carolina -
South Dakota -
Tennessee -
Texas -
Utah -
Vermont -
Virginia - Washington
- Washington-DC
-
West Virginia -
Wisconsin -
Wyoming |
| Find out about latest termite control methods - Click here |
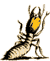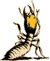

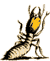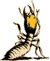

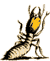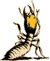

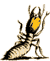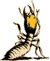

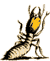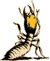

| www.termite.com © copyright 1995 - |