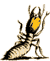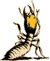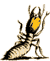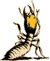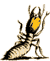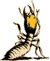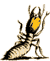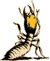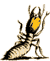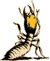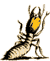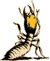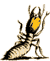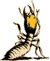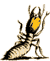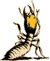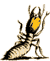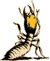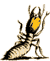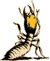Where do You find them ? Native to the US, the Western drywood
termites are found accross the southwestern states, and as far north as
Sacramento, with a heavier incidence along the coastal areas.
Drywood
termites are considered non-subterranean termites, as they do not live
in the ground, require no ground contact, and do not build mud shelter tubes.
Can you bring them into the home in furniture ? YES - Western drywood
termites can be transported in infested timber furniture or even picture
frames. This termite can survive inside timber with a low moisture content
and can branch off to form multiple independent colonies, each containing
up to 3,000 termites. They are known to cause extensive damage in buildings.
Are all types of buildings prone ? Western drywood termites more likely
to be in a structure made completely of wood with poor workmanship demonstrated
by poorly fitted corner joints. The termites typically inter the ends
of wood and seldom enter the sides of the section in question.
After the mating flight, they
seek cracks or knotholes in nearby wood and chew a small tunnel which
they close then excavating a chamber after which they mate.
Swarming drywood termites fly
into structures and infest wood directly. When swarming, they often reinfest
the same structure. They typically first infest exposed wood such as window/door
frames, trim, eaves and attics. They do so by finding a protected crevice
or other area, such as the joint between 2 pieces of wood, where shingles/paper
overhang timber or moulding, etc., and then attack the wood.
Evidence of infestation include swarmers, shed wings, piles of pellets,
termite plugs that seal all openings in infested wood, and surface blisters
caused by older, enlarged galleries very close to the wood surface.
Identification: Swarmers are about 1/2'' long including wings, which are approx
3/8" long. The head and pronotum of the swarmer is an orange brown
and its abdomen is dark brown - see picture on left.
Key identifier: The front wing has 3 dark, heavily hardened veins
in the front portion.
When the colony is about four years old it will, when the time is
right, emit hundreds of reproductive swarmers from the nest. It
is amazing how all the mature Wester drywood termite colony nests
across an entire region, will swarm several times a year, but all
at the same time. This is essential to produce new nests, to continue
their 250 million year evolution.
Swarming typically takes place about mid-day on sunny, warm (80°F)
days, with the peak of the swarm occurring shortly after a sudden
rise in temperature. The swarming season usually occurs during September
and October. Swarmers usually number in the dozens, occasionally
the hundreds. Night swarmers are attracted to lights. |
Identification: Soldiers, the forehead of which slopes down gradually
from top of head. The head is flattened to slightly rounded in side
view. The head is orange to reddish brown with the eye spot whitish
- see picture on the left.
Soldiers have mandibles with unequal number of teeth on each member
of pair, and antenna with the third segment greatly enlarged and
club-like - as indicated by the red arrow in the picture to the
left.
The soldiers are the defenders against intruders so if you open
up timbers containing a drywood infestation it is the soldiers that
first rush out to guard and defend the other colony members.
Although the colony development is slow, severe structural damage
may still be caused by the presence of multiple-colonies. Their
gallery and tunnel walls are velvety smooth, and no soil is present,
unlike subterranean termites.
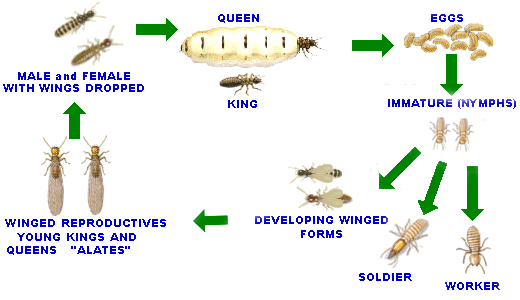
Another key identifier is that there is no workers present in Western
drywood termite infestations; it is the nymphs perform all tasks
typically done by workers. |
Identification: Timber Damage: Drywood termites eat across the wood grain
and create chambers, or galleries connected by tunnels. Although the colony
development is slow, severe structural damage may still be caused by the
presence of multiple-colonies. Their gallery and tunnel walls are velvety
smooth, and no soil is present, unlike subterranean termites. A distinctive
indication is no presence of a worker caste and the nymphs perform all
tasks typically done by workers.
Identification: Faecal pellets are found throughout their tunnels. Generally,
there are faeal pellets present. They are hard, less than 1/32'' long,
elongate-oval with rounded ends. One of the unusual distinctive signs
of their faecal pellets is that they have 6 concave sides.
Termite Control: Western drywood termites - firstly, obtain a professional
termite inspection to determine the extent of an infestation and locations
of other possible drywood termite colonies. The results of the inspection
will dictate the best treatment options as no single control method is
best for all situations.
Where the infestation is severe and extensive - the entire building may
need to be fumigated wtth sulfuryl fluoride (Vikane.). Fumigation is a
highly technical procedure which involves surrounding the structure with
a gas-tight tarpaulin, releasing the gas inside the seal, and aerating
the fumigant after a set exposure time. Before fumigation, the homeowner
must remove all plants and animals from the house, remove or place food
items inside special protective bags, and insure that there is sufficient
tarp clearance between sensitive landscaping and exterior walls.
Where the infestation is only loacalised - it may sufficient to effect
localise spot tretments of the termute colony. An insecticide is injected
into small holes drilled in the timber and into termite galleries. This
is the simplest and most direct method of treatment. The amount of drilling
required and the effectiveness of this treatment depends on the chemical
used and the nature of the infestation.
Links to other websites:
Clemson
University -
Drywood
Termites -
TAMU
University -
Termite
Control Pesticides -
University
of Arizona